DI Martin Schmidt

I hold a Master's degree in Financial and Actuarial Mathematics from the Vienna University of Technology (graduation with highest distinction) and have been working as a Quantitative Credit Risk Manager within an international banking group in Austria for more than 4 years. In 2020, I joined the National Bank of Austria as an Examiner for IRB credit risk models of significant financial institutions. I have excellent programming and database (Python, R, SAS, SQL, VBA) as well as statistical/mathematical skills and gained hands-on machine learning experience during various Data Science Hackathons (amongst others: Winner of the ‘Coding Challenge on Risk Management‘ hosted by the European Central Bank).
NLP - Topic Modeling (Python)
Purpose
For this project I have scraped (see my scraping tutorial here) news articles from Reuters and clustered them using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA).
Since there is no proper classification of articles on Reuters, my model supports the reader in finding articles relating to a specific topic. Furthermore, the model could be used to classify future articles as well.
1 - Data Gathering
I used the scraper i described here to get all available Euro-Zone news from Reuters.
The data can be downloaded from here.
2 - Required Packages
import logging
logging.captureWarnings(True)
# Data Processing
from collections import Counter
import datetime as dt
from dateutil.relativedelta import relativedelta
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import pyLDAvis
import pyLDAvis.sklearn
from wordcloud import WordCloud
# NLP
import gensim
from nltk.stem import SnowballStemmer
from nltk.util import ngrams
import spacy
# Modeling
from sklearn.decomposition import LatentDirichletAllocation
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
3 - Data Cleaning
In this step i read the data into a pandas dataframe, clean missing values and convert dates stored in strings to actual dates.
3.1 - Custom Functions
def read_data_from_csv(path_to_data, sep=";"):
df = pd.read_csv(path_to_data, sep=sep)
print(f"shape of df: {df.shape}")
print(f"columns in df: {list(df.columns)}")
return df
def drop_rows_with_missing_values(df):
rows_orig = df.shape[0]
df = df.dropna().reset_index(drop=True)
print(f"{rows_orig-df.shape[0]} rows dropped")
print(f"new shape of df: {df.shape}")
return df
def convert_date_ReutersNews(df, date_col):
df = df[df.scraper == "reuters_news"].copy()
month_map = {
"January":1, "February":2, "March":3,
"April":4, "May":5, "June":6,
"July":7, "August":8, "September":9,
"October":10, "November":11, "December":12
}
regex_date = r"([A-Z]\w+) (\d+), (\d+)"
mdy = df[date_col].str.extract(regex_date)
df["month"] = mdy[0].map(month_map)
df["day"] = mdy[1]
df["year"] = mdy[2]
df[date_col] = pd.to_datetime(df[['year', 'month', 'day']])
df = df.drop(['year', 'month', 'day'], axis=1).reset_index(drop=True)
return df
def convert_dates(df, date_col):
df_Reuters = convert_date_ReutersNews(df, date_col)
df_full = pd.concat([df_Reuters])
print(f"shape of df: {df_full.shape}")
print(f"columns in df: {list(df_full.columns)}")
return df_full
3.2 - Read Data
path_data = "../data/20200329_reuters_news_euro_zone.csv"
df = read_data_from_csv(path_data)
shape of df: (9773, 5)
columns in df: ['scraper', 'url', 'date', 'title', 'text']
df[["date", "title", "text"]].head(3)
| date | title | text | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | July 24, 2018 / 8:08 PM / in 3 months | Reuters Leadership | Jane Barrett Rob Cox... |
| 1 | March 28, 2020 / 4:15 PM / Updated 14 hours ago | Coronavirus death toll in Italy's Lombardy ris... | MILAN (Reuters) - The death toll from an outbr... |
| 2 | March 28, 2020 / 10:01 PM / Updated 10 hours ago | Northern Ireland brings in tough measures to f... | BELFAST (Reuters) - Northern Ireland will intr... |
3.3 - Missing Value Treatment
I decided to drop all rows with missing values
df.isnull().sum()
scraper 0
url 0
date 54
title 54
text 1
dtype: int64
df = drop_rows_with_missing_values(df)
55 rows dropped
new shape of df: (9718, 5)
3.4 - Converting to Actual Dates
The scraped date has the following form: ‘Month DD, YYYY …’. Since this can’t be properly used as a date, I used RegEx to parse the date from these strings.
df.date.iloc[0]
'July 24, 2018 / 8:08 PM / in 3 months'
df = convert_dates(df, "date")
shape of df: (9718, 5)
columns in df: ['scraper', 'url', 'date', 'title', 'text']
df.date.iloc[0]
Timestamp('2018-07-24 00:00:00')
4 - Exploratory Data Analysis
In this step i looked at published articles over time and futher cleaned the data based on the graphical results. This step is mainly necessary, because over time some of the older news articles are no longer available.
4.1 - Custom Functions
def keep_only_articles_published_after(df, date_col, date_min):
rows_orig = df.shape[0]
df = df[df[date_col] >= date_min].copy().reset_index(drop=True)
print(f"{rows_orig-df.shape[0]} rows dropped")
print(f"new shape of df: {df.shape}")
return df
4.2 - Further Data Cleaning based on Publication Date
df_plot = df.date.value_counts().sort_index().reset_index()
df_plot.columns = ["date", "articles"]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,3))
plt.hist(df_plot.date, bins=(df_plot.date.max()-df_plot.date.min()).days+1)
plt.title('Dates w/o Publications', fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel('publication date')
plt.gca().axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()

This plot clearly shows that some articles published before 09/2018 are no longer available online. The next graphic confirms this.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,3))
plt.plot(df_plot.date, df_plot.articles)
plt.title('Published Articles over Time', fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel('publication date')
plt.ylabel('articles')
plt.show()
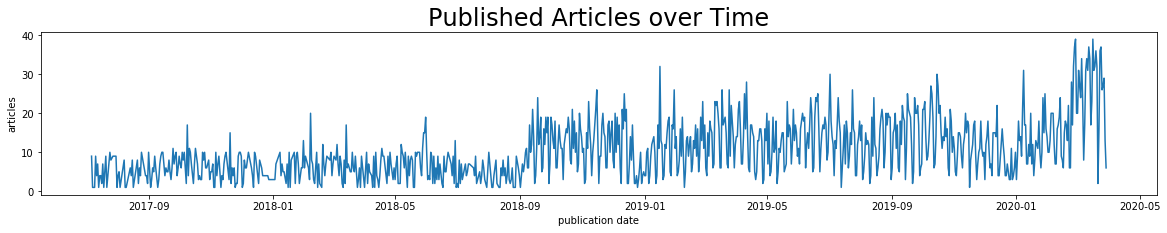
I have decided to not consider articles before September 2018 for this project.
date_min = dt.datetime(2018,9,1)
df = keep_only_articles_published_after(df, "date", date_min)
2000 rows dropped
new shape of df: (7718, 5)
After all these steps we reduced numbers of articles by 2,055 and are left with 7,718 articles over a time period of 1.5 years.
5 - Feature Engineering
I performed the following steps for feature engineering and text-data cleaning:
- Special character replacement
- Tokenization using gensim.utils.simple_preprocess
- Most of the articles have the following beginning: “Some-City (Reuters) - “. I decided to remove this pre-article information by searching for “reuters” and deleting all tokens before this keyword
- Lemmatization with POS-tagging using spacy’s “en_core_web_lg” (optional)
- Stemming using nltk’s “SnowballStemmer” (optional)
- Removing short words (min. word length can be specified) and stop-words
- Adding N-Grams (optional)
5.1 - Custom Functions
def remove_shortest_longest_articles(tokens, remove_lowest, remove_highest):
orig_shape = tokens.shape
article_length = tokens.apply(lambda x: len(x))
article_length_vc = article_length.value_counts().sort_index().cumsum()/tokens.shape[0]
remove_len = article_length_vc[(article_length_vc <= remove_lowest) | (1-article_length_vc <= remove_highest)].index
tokens = tokens[~np.isin(article_length, remove_len)] # .reset_index(drop=True)
print(f"{orig_shape[0]-tokens.shape[0]} articles dropped.")
print(f"{tokens.shape[0]} articles remaining for modeling.")
return tokens
5.2 - Create Final Tokens for Modeling
def preprocess_text(txt,
spacy_lang_obj,
min_word_length=3,
lemmatize=True,
stem=True,
ngrams_n_list=[2]):
"""
Preprocessing of text/titles
Input:
- txt: string - text/title
- spacy_lang_obj = spacy.load("en_core_web_XX")
- min_word_length: integer - keep only words with length >= min_word_length
- lemmatize: boolean - if True then lemmatize tokens
- stem: boolean - if True then stem tokens
- ngrams_n_list - list of integers, if ngrams not wanted, pass empty list []
"""
# spacy language tokenizer, tagger, parser, ner and word vectors
nlp = spacy_lang_obj
# replace special characters
special_chars = {"ö":"oe", "ä":"ae", "ü":"ue", "ß":"ss"}
for char in special_chars:
txt = txt.replace(char,special_chars[char])
# split text into tokens
tokens = gensim.utils.simple_preprocess(txt, deacc=True)
# remove pre-article information (mostly cities)
ind_reuters = tokens.index("reuters") if "reuters" in tokens else -1
if ind_reuters > 5:
ind_reuters = -1
tokens = tokens[ind_reuters+1:]
# lemmatize tokens using spacy
if lemmatize == True:
full_text = nlp(" ".join(tokens))
tokens = [token.lemma_ for token in full_text if token.pos_ in ['NOUN', 'ADJ', 'VERB', 'ADV']]
# stem tokens using SnowballStemmer from nltk
if stem == True:
stemmer = SnowballStemmer('english')
tokens = [stemmer.stem(token) for token in tokens]
# keep only tokens with length >= min_word_length
tokens = [token for token in tokens if len(token) >= min_word_length]
# remove stop-words from tokens
tokens_wo_stopwords = []
for token in tokens:
if (nlp.vocab[token].is_stop == False) & (~np.isin(token, ["reuters", "reuter"])):
tokens_wo_stopwords.append(token)
# build n-grams
ngram_list = []
if ngrams_n_list != []:
for n in ngrams_n_list:
if n > 1:
for ngram in ngrams(tokens_wo_stopwords, n):
ngram_list.append("_".join(str(i) for i in ngram))
# final list of tokens
tokens_final = tokens_wo_stopwords + ngram_list
return tokens_final
Load Spacy’s pretrained statistical model for English.
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_lg")
For my model I decided to
- set min_word_length to 3,
- skip stemming and
- use bigrams.
tokens_final = df.text.apply(
lambda x: preprocess_text(
txt=x,
spacy_lang_obj=nlp,
min_word_length=3,
lemmatize=True,
stem=False,
ngrams_n_list=[2]
)
)
tokens_final.head(3)
0 [death, toll, outbreak, coronavirus, northern,...
1 [introduce, sweeping, new, power, combat, spre...
2 [team, minister, win, test, coronavirus, sympt...
Name: text, dtype: object
5.3 - Publication-Length: Outlier Treatment
Note that the lengths include bigrams as well
tokens_len = tokens_final.apply(lambda x: len(x))
print(f"min. publication length: {min(tokens_len)}")
print(f"max. publication length: {max(tokens_len)}")
min. publication length: 7
max. publication length: 5281
Looking at the distribution of articles-lengths yields the following (for the plot I excluded articles with >1,000 words):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
tokens_len[tokens_len <= 1000].hist(bins=200)
plt.show()
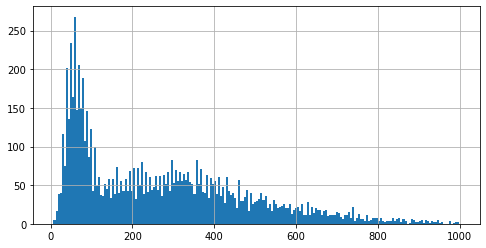
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
tokens_len[tokens_len <= 100].hist(bins=40)
plt.show()
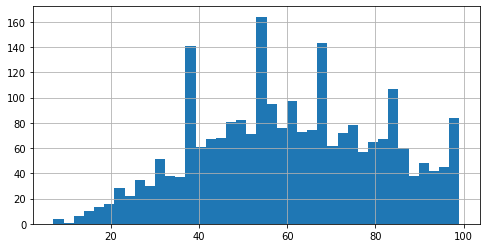
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
tokens_len[tokens_len > 1000].hist()
plt.show()
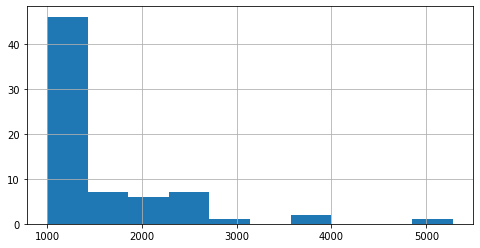
Based on the above and further analysis I have decided to exclude the top 1% of the short/longest articles. This leaves us with 7580 publications for modeling.
tokens_final = remove_shortest_longest_articles(tokens_final, 0.01, 0.01)
138 articles dropped.
7580 articles remaining for modeling.
5.4 - Vocabulary
We now have a look at the vocabulary we will later pass to the model.
# split vocabulary into uni- and bi-grams
unigrams = [word for words in tokens_final for word in words if not "_" in word]
bigrams = [word for words in tokens_final for word in words if "_" in word]
print(f"total number of words: {len(unigrams)}")
print(f"total number of bigrams: {len(bigrams)}")
total number of words: 1027221
total number of bigrams: 1019657
# unique words and bigrams in our train-dataset
unigrams_unique = sorted(list(set(unigrams)))
bigrams_unique = sorted(list(set(bigrams)))
print(f"unique words: {len(unigrams_unique)}")
print(f"unique bigrams: {len(bigrams_unique)}")
unique words: 17957
unique bigrams: 577945
most_used_unigrams = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(Counter(unigrams), orient="index").reset_index()
most_used_unigrams.columns = ["word", "occurence"]
most_used_unigrams.sort_values(by="occurence", inplace=True)
most_used_unigrams.tail(5)
| word | occurence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1029 | percent | 4685 |
| 135 | tell | 4708 |
| 620 | deal | 5514 |
| 61 | government | 7004 |
| 203 | year | 10035 |
most_used_bigrams = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(Counter(bigrams), orient="index").reset_index()
most_used_bigrams.columns = ["word", "occurence"]
most_used_bigrams.sort_values(by="occurence", inplace=True)
most_used_bigrams.tail(5)
| word | occurence | |
|---|---|---|
| 199 | news_conference | 476 |
| 2370 | central_bank | 588 |
| 3211 | year_old | 656 |
| 8371 | interest_rate | 776 |
| 598 | tell_reporter | 862 |
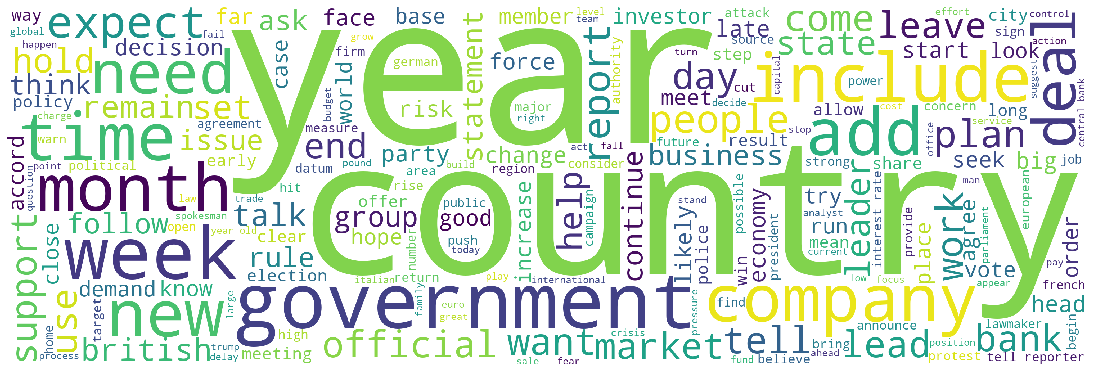
wordcloud_unigrams = WordCloud(
width=3000,
height=1000,
background_color="white",
min_font_size = 12
).generate(" ".join(unigrams))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.imshow(wordcloud_unigrams)
plt.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout(pad=0)
6 - Modeling
6.1 - Create Document-Term Matrix
corpus = tokens_final.apply(lambda x: " ".join(x))
# only count words that appear in more than 15 articles
# don't count words that appear in more than 75% of articles
cv = CountVectorizer(min_df=15, max_df=0.75)
document_term_matrix = cv.fit_transform(corpus)
6.2 - Baseline Model
lda_baseline = LatentDirichletAllocation(n_jobs=-1).fit(document_term_matrix)
print("------ Baseline Model ------")
# print(f"perplexity: {round(lda_baseline.perplexity(document_term_matrix),2)}") # see comment in 6.3.2
print(f"log_likelihood: {round(lda_baseline.score(document_term_matrix),2)}")
------ Baseline Model ------
log_likelihood: -8421569.0
6.3 - Grid-Search to find optimal parameters
6.3.1 - Log-Likelihood
topic_models_ll = GridSearchCV(
estimator=LatentDirichletAllocation(n_jobs=-1),
param_grid={"n_components": list(range(10, 41, 2)),
"learning_decay": [0.5, 0.7, 0.9]},
cv=[(slice(None), slice(None))], # no cv for unsupervised ml
n_jobs=-1,
verbose=20
)
topic_models_ll.fit(document_term_matrix)
print("---------------- Best Model (Log-Likelihood) ----------------")
print(f"model parameters: {topic_models_ll.best_params_}")
# print(f"perplexity: {round(topic_models_ll.best_estimator_.perplexity(document_term_matrix),2)}") # see comment in 6.3.2
print(f"log_likelihood: {round(topic_models_ll.best_estimator_.score(document_term_matrix),2)}")
---------------- Best Model (Log-Likelihood) ----------------
model parameters: {'learning_decay': 0.5, 'n_components': 28}
log_likelihood: -8385793.37
models_ll = pd.DataFrame(topic_models_ll.cv_results_)
models_ll = models_ll[["param_learning_decay", "param_n_components", "mean_test_score"]]
models_ll.rename(columns={'mean_test_score':'log_likelihood'}, inplace=True)
models_ll.sort_values(by="log_likelihood", ascending=False, inplace=True)
# top models (log likelihood)
models_ll.head(5)
| param_learning_decay | param_n_components | log_likelihood | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 0.5 | 28 | -8.360676e+06 |
| 24 | 0.7 | 26 | -8.362038e+06 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 26 | -8.365602e+06 |
| 22 | 0.7 | 22 | -8.367235e+06 |
| 38 | 0.9 | 22 | -8.369719e+06 |
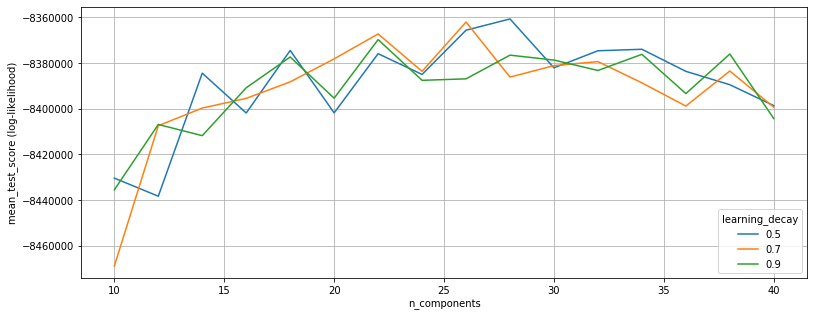
df_plot = pd.DataFrame(topic_models_ll.cv_results_)
n_topics = list(range(10,41,2))
ld5 = df_plot[(df_plot.param_learning_decay==0.5)].mean_test_score.tolist()
ld7 = df_plot[(df_plot.param_learning_decay==0.7)].mean_test_score.tolist()
ld9 = df_plot[(df_plot.param_learning_decay==0.9)].mean_test_score.tolist()
plt.figure(figsize=(13, 5))
plt.plot(n_topics, ld5, label="0.5")
plt.plot(n_topics, ld7, label="0.7")
plt.plot(n_topics, ld9, label="0.9")
plt.xlabel("n_components")
plt.ylabel("mean_test_score (log-likelihood)")
plt.legend(title='learning_decay', loc='lower right')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
6.3.2 - Perplexity
Extend the LDA class in order to use perplexity as score. Currently not possible, as there seems to be a bug in sklearn.
6.4 - Model Choice and Visualization
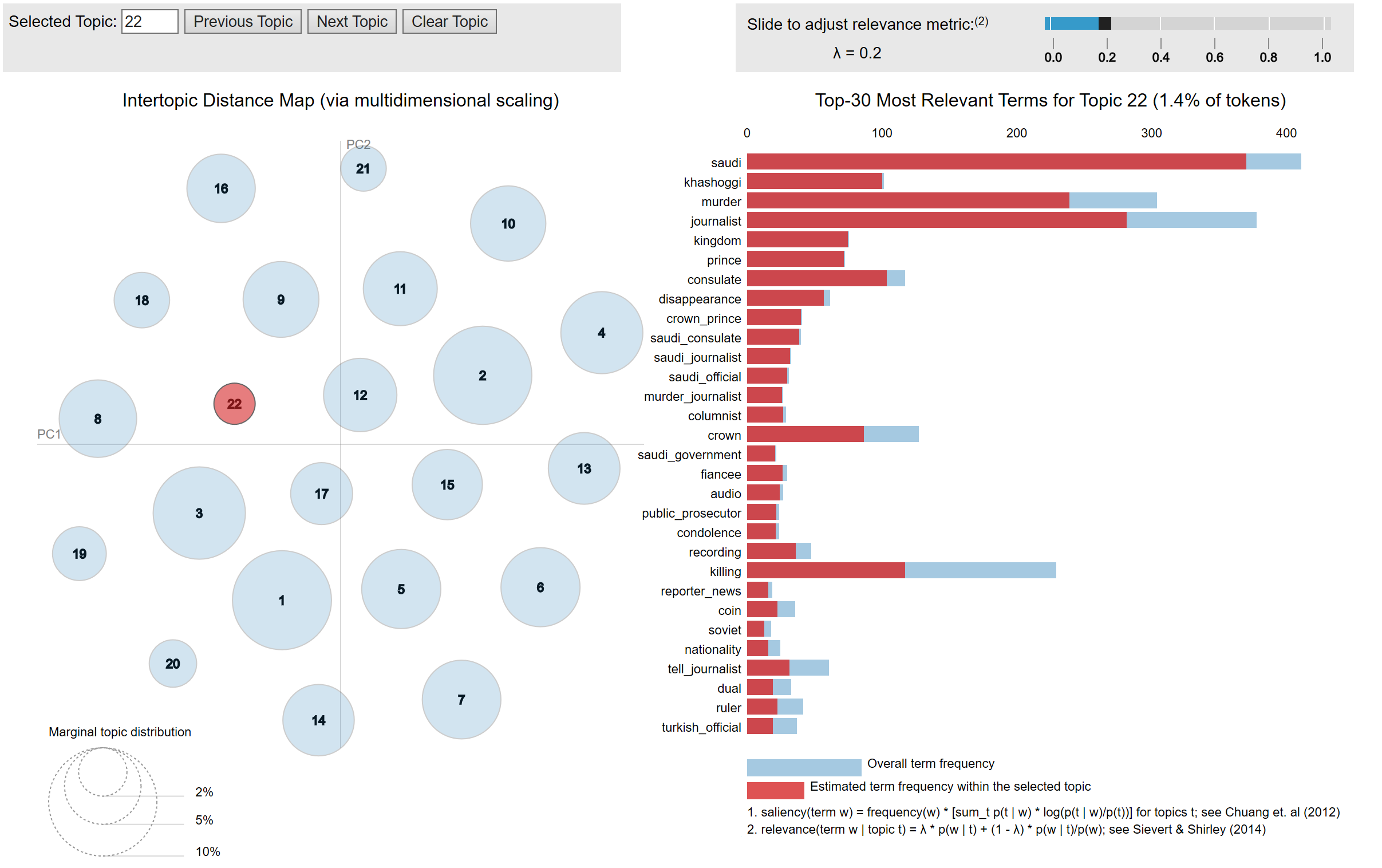
I decided to not go with the model suggested via Grid-Search and chose the model with n_components=22 and learning_decay=0.7 instead (4th-best model). The main reason for this is that the difference to a model with more topics (28 in the best case) is not too significant.
lda_final = LatentDirichletAllocation(
n_components=22,
learning_decay=0.7,
n_jobs=-1
).fit(document_term_matrix)
I used pyLDAvis for visualization purposes. I have saved the results as HTML and they can be viewed here.
pyLDAvis.enable_notebook()
panel = pyLDAvis.sklearn.prepare(lda_final, document_term_matrix, cv, mds='tsne')
pyLDAvis.save_html(panel, 'lda_final.html')
7 - Final Dataframe including Topic
topic = np.argmax(lda_final.transform(document_term_matrix), axis=1)+1
tok_cor_top = pd.DataFrame(
data={"corpus": corpus, "tokens": tokens_final, "topic": topic},
index=corpus.index
)
df_topics = df.merge(tok_cor_top, left_index=True, right_index=True, how="inner").reset_index(drop=True)
df_topics[["date", "title", "text", "topic"]].head()
| date | title | text | topic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-03-28 | Coronavirus death toll in Italy's Lombardy ris... | MILAN (Reuters) - The death toll from an outbr... | 12 |
| 1 | 2020-03-28 | Northern Ireland brings in tough measures to f... | BELFAST (Reuters) - Northern Ireland will intr... | 12 |
| 2 | 2020-03-27 | British ministers won't be tested for virus un... | LONDON (Reuters) - Boris Johnson’s top team of... | 12 |
| 3 | 2020-03-27 | Johnson's central role to UK virus response en... | LONDON (Reuters) - People with a central role ... | 12 |
| 4 | 2020-03-27 | Foreigners face suspicion in China as coronavi... | SHENZHEN, China/SHANGHAI (Reuters) - Francesca... | 12 |