DI Martin Schmidt

I hold a Master's degree in Financial and Actuarial Mathematics from the Vienna University of Technology (graduation with highest distinction) and have been working as a Quantitative Credit Risk Manager within an international banking group in Austria for more than 4 years. In 2020, I joined the National Bank of Austria as an Examiner for IRB credit risk models of significant financial institutions. I have excellent programming and database (Python, R, SAS, SQL, VBA) as well as statistical/mathematical skills and gained hands-on machine learning experience during various Data Science Hackathons (amongst others: Winner of the ‘Coding Challenge on Risk Management‘ hosted by the European Central Bank).
Diploma Thesis
Aggregation of Integer-Valued Risks with Copula-Induced Dependency Structure
1. Abstract
In this diploma thesis we investigate a portfolio of d integer-valued risks and calculate the distribution of the aggregate loss S, which is the sum of these. To generalize the popular assumption of independence used in practice, we model the dependency structure of the individual risks using copulas, allowing for a wide range of flexibility. After a rather detailed introduction to copula theory, the main part of this thesis starts with a formula for the distribution function of S. In addition, a recursion formula for the probability mass function of S is provided. Bounds on the distribution of S determined by the Rearrangement Algorithm serve to quantify the model risk caused by feasible scenarios of dependency. To illustrate the theoretical considerations, the final chapter contains a multitude of numerical examples in which, besides the distribution and probability mass function, common risk measures such as Value-at-Risk and Expected Shortfall for S are calculated under various dependency structures.
2. Full Text and Evaluation
View the thesis here.
View the evaluation here.
3. Summary of the Main Results
View the summary here.
4. Some Numerical Results
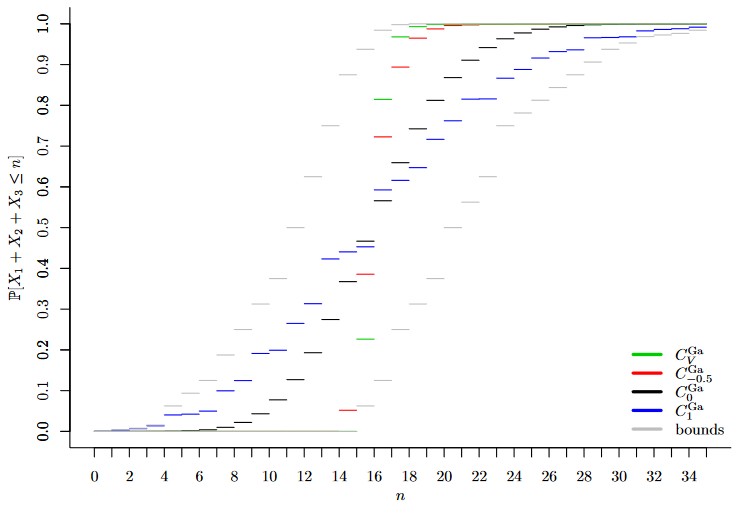
- Distribution Function of the sum S of three Poisson-distributed random variables under different dependency scenarios (using Gaussian Copulas).
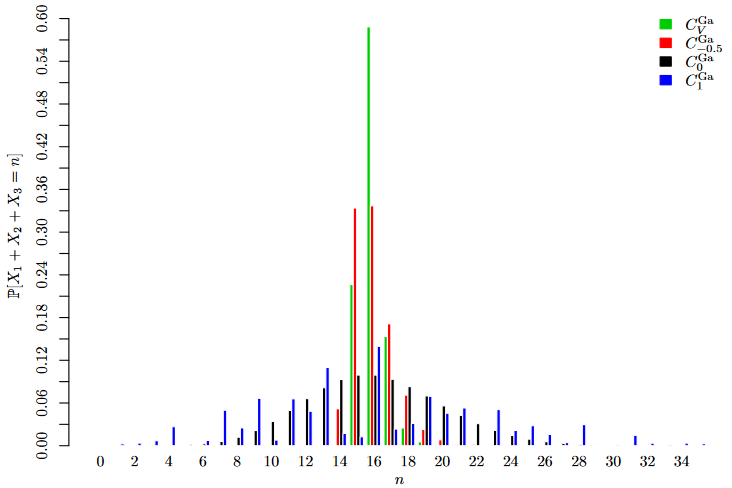
- Probability Mass Function of the sum S of three Poisson-distributed random variables under different dependency scenarios (using Gaussian Copulas).
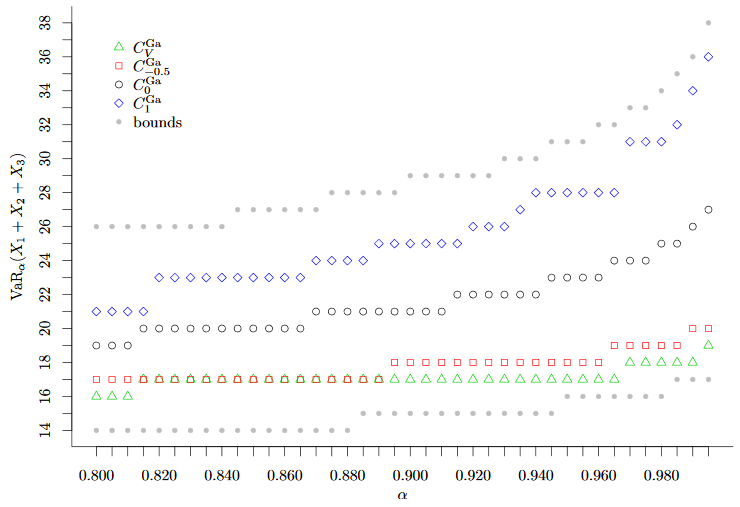
- Value-at-Risk of the sum S of three Poisson-distributed random variables under different dependency scenarios (using Gaussian Copulas).
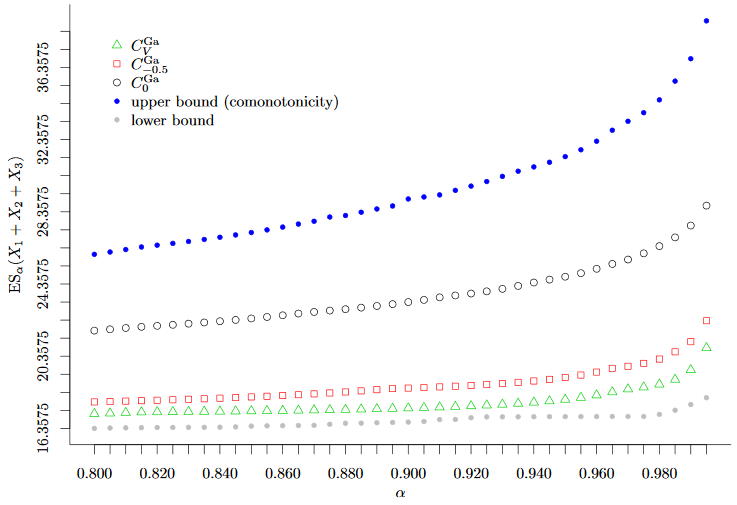
- Expected Shortfall of the sum S of three Poisson-distributed random variables under different dependency scenarios (using Gaussian Copulas).
5. R-Code
In this section I provide different R codes for calculation of the numerical results presented in the diploma thesis.
- 5.1. Calculation of the Distribution Function of the Aggregate Loss S
- 5.2. Recursion for the Calculation of the Probability Mass Function of the Aggregate Loss S
- 5.3. Calculation of the Probability Mass Function of the Aggregate Loss S by Integration over Copula Densities
- 5.4. Rearrangement Algorithm for the Calculation of Sharp Bounds on the Distribution of the Aggregate Loss S
- 5.5. Calculation of Sharp Bounds on Value-at-Risk and Expected Shortfall
5.1. Calculation of the Distribution Function of the Aggregate Loss S

helper.evalCopula=function(j,copula,margins) {
valMargins=numeric(length(j))
for (i in 1:length(valMargins)) {
valMargins[i]=margins[[i]](j[i])
}
return(copula(valMargins))
}
helper.setNextCombination=function(j,target) {
for (i in 1:length(j)) {
j[i]=j[i]+1
if (j[i]<=target&&sum(j)<=target) {
break
} else {
j[i]=0
}
}
return(j)
}
S.distribution=function(d,n,copula,margins) {
if (n<0) {
return(0)
}
n=floor(n)
j=numeric(d)
result=0
for (k in 0:min(d-1,n)) {
j=numeric(d)
if (sum(j)==n-k) {
result=result+((-1)^k)*choose(d-1,k)*helper.evalCopula(j,copula,margins)
}
repeat {
j=helper.setNextCombination(j,n-k)
if (sum(j)==0) {
break
} else if (sum(j)==n-k) {
result=result+((-1)^k)*choose(d-1,k)*helper.evalCopula(j,copula,margins)
}
}
}
return(result)
}
5.2. Recursion for the Calculation of the Probability Mass Function of the Aggregate Loss S

helper.setNextIndex=function(ind,maxValues) {
for (i in 1:length(ind)) {
ind[i]=ind[i]+1
if (ind[i]<=maxValues[i]) {
break
} else {
ind[i]=1
}
}
return(ind)
}
helper.calcCombinations=function(d,n,support) {
j=numeric(d)
ind=rep(1,d)
number=1
maxValues=numeric(d)
combinations=list()
for (i in 1:d) {
maxValues[i]=length(support[[i]])
}
repeat {
for (i in 1:d) {
j[i]=support[[i]][ind[i]]
}
if (sum(j)<=n) {
combinations[[number]]=c(sum(j),j)
number=number+1
}
ind=helper.setNextIndex(ind,maxValues)
if (sum(ind)==d) {
break
}
}
return(combinations)
}
S.probabilityMassFunctionRecursion=function(d,n,copula,margins,support,combinations=list(),firstRun=TRUE) {
result=NULL
valMargins=numeric(d)
combinationsN = list()
ind=1
if(firstRun==TRUE) {
combinations=helper.calcCombinations(d,n,support)
}
uniqueComb=NULL
for (i in 1:length(combinations)) {
uniqueComb[i]=combinations[[i]][1]
}
if (sum(uniqueComb==n)==0) {
return(0)
}
if (n==0) {
for (i in 1:d) {
valMargins[i]=margins[[i]](0)
}
result=copula(valMargins)
return(result)
} else {
for (i in 1:length(combinations)) {
if(combinations[[i]][1]==n) {
combinationsN[[ind]]=combinations[[i]][2:(d+1)]
ind=ind+1
}
}
if (length(combinationsN)==0) {
return(0)
} else {
tmpCopula=0
tmpSum=0
for (i in 1:length(combinationsN)) {
for (k in 1:d) {
valMargins[k]=margins[[k]](combinationsN[[i]][k])
}
tmpCopula=tmpCopula+copula(valMargins)
}
for (k in 1:n) {
tmpSum=tmpSum+choose(k+d-1,d-1)*S.probabilityMassFunctionRecursion(d,n-k,copula,margins,support,combinations,FALSE)
}
result=tmpCopula-tmpSum
return(result)
}
}
}
5.3. Calculation of the Probability Mass Function of the Aggregate Loss S by Integration over Copula Densities

library("cubature")
helper.setNextIndex=function(ind,maxValues) {
for (i in 1:length(ind)) {
ind[i]=ind[i]+1
if (ind[i]<=maxValues[i]) {
break
} else {
ind[i]=1
}
}
return(ind)
}
helper.calcCombinations=function(d,n,support) {
j=numeric(d)
ind=rep(1,d)
number=1
maxValues=numeric(d)
combinations=list()
for (i in 1:d) {
maxValues[i]=length(support[[i]])
}
repeat {
for (i in 1:d) {
j[i]=support[[i]][ind[i]]
}
if (sum(j)==n) {
combinations[[number]]=j
number=number+1
}
ind=helper.setNextIndex(ind,maxValues)
if (sum(ind)==d) {
break
}
}
return(combinations)
}
S.probabilityMassFunctionIntegration=function(d,n,copulaDensity,margins,support) {
J=helper.calcCombinations(d,n,support)
result=0
for (j in J) {
limUpper=NULL
limLower=NULL
for (i in 1:length(j)) {
limUpper[i]=margins[[i]](j[i])
limLower[i]=margins[[i]](j[i]-1)
}
int=adaptIntegrate(copulaDensity,lowerLimit=limLower,upperLimit=limUpper)
result=result+int$integral
}
return(result)
}
5.4. Rearrangement Algorithm for the Calculation of Sharp Bounds on the Distribution of the Aggregate Loss S

helper.rearrangeMatrix=function(d,M,tolerance,func) {
M=apply(M,2,sample)
absDiff=Inf
result=Inf
while(absDiff>tolerance) {
tmp=result
for (j in 1:d) {
rankBy=rowSums(M[,(1:d)[-j]])
M[,j]=sort(M[,j],decreasing=TRUE)[rank(rankBy)]
}
result=func(rowSums(M))
absDiff=abs(result-tmp)
}
return(result)
}
S.upperBound=function(d,n,quantiles,tolerance,N) {
left=0
right=1
repeat {
result=(left+right)/2
X=matrix(ncol=d,nrow=N)
for (i in 1:N) {
for (j in 1:d) {
X[i,j]=quantiles[[j]](result*(i-1)/N)
}
}
nApprox=helper.rearrangeMatrix(d,X,tolerance,max)
if (abs(n+1-nApprox)<tolerance||abs(left-right)<tolerance) {
break
}
if (nApprox>n+1) {
left=result*2-right
right=result
} else {
right=result*2-left
left=result
}
}
return(result)
}
S.lowerBound=function(d,n,quantiles,tolerance,N) {
left=0
right=1
repeat {
result=(left+right)/2
X = matrix(ncol=d,nrow=N)
for (i in 1:N) {
for (j in 1:d) {
X[i,j]=quantiles[[j]](result+(1-result)*(i-1)/N)
}
}
nApprox=helper.rearrangeMatrix(d,X,tolerance,min)
if (abs(n+1-nApprox)<tolerance||abs(left-right)<tolerance) {
break
}
if (nApprox<n+1) {
right=result*2-left
left=result
} else {
left=result*2-right
right=result
}
}
return(result)
}
5.5. Calculation of Sharp Bounds on Value-at-Risk and Expected Shortfall

VaR.lowerBound=function(quantiles,tolerance,alpha,N,d) {
iterations=1e2
X=matrix(0,nrow=N,ncol=d)
for (j in 1:d) {
for (i in 1:N) {
X[i,j]=quantiles[[j]]((alpha*(i-1))/N)
}
}
X=apply(X,2,sample)
VaR_L=-Inf
for (i in 1:iterations) {
for (j in 1:d) {
rankBy=rowSums(X[,(1:d)[-j]])
X[,j]=sort(X[,j],decreasing=TRUE)[rank(rankBy)]
}
tmp=max(rowSums(X))
if (tmp>VaR_L) {
VaR_L=tmp
}
}
return(VaR_L)
}
VaR.upperBound=function(quantiles,tolerance,alpha,N,d) {
iterations=1e2
X=matrix(0,nrow=N,ncol=d)
for (j in 1:d) {
for (i in 1:N) {
X[i,j]=quantiles[[j]]((alpha)+((1-alpha)*i)/N)
}
}
X=apply(X,2,sample)
VaR_U=Inf
for (i in 1:iterations) {
for (j in 1:d) {
rankBy=rowSums(X[,(1:d)[-j]])
X[,j]=sort(X[,j],decreasing=TRUE)[rank(rankBy)]
}
tmp=min(rowSums(X))
if (tmp<VaR_U) {
VaR_U=tmp
}
}
return(VaR_U)
}
ES.lowerBound=function(quantiles,tolerance,alpha,N,d) {
iterations=1e2
X=matrix(0,nrow=N,ncol=d)
for (j in 1:d) {
for (i in 1:N) {
X[i,j]=quantiles[[j]]((i-1)/N)
}
}
X=apply(X,2,sample)
ES_L=-Inf
for (i in 1:iterations) {
for (j in 1:d) {
rankBy=rowSums(X[,(1:d)[-j]])
X[,j]=sort(X[,j],decreasing=TRUE)[rank(rankBy)]
}
Y=sort(rowSums(X))
tmp=sum(Y[(floor(N*alpha)+1):N])/(N*(1-alpha))
if (tmp>ES_L) {
ES_L=tmp
}
}
return(ES_L)
}
ES.upperBound=function(quantiles,alpha,N,d) {
helper.univariateES=function(qDist,N,alpha) {
X=matrix(0,nrow=N)
for (i in 1:N) {
X[i]=qDist(alpha+((1-alpha)*(i-1))/N)
}
return(sum(X)/N)
}
tmp=numeric(d)
for (j in 1:d) {
tmp[j]=helper.univariateES(quantiles[[j]],N,alpha)
}
ES_U=sum(tmp)
return(ES_U)
}